As science spreads its mighty wings ever further, the view we generate of the world around us becomes clearer and clearer. Recently we posted the biggest picture of the universe that has ever been taken, today we travel the opposite direction and take a searingly intimate look at our inner selves.
Medical science has been roaring into the future since its inception and Revolution CT is the newest and sharpest innovation in the field of medical imaging. In the past taking a clear and reliable scan of a patient has been possible, but tricky. Normal imaging techniques work amazingly well if the patient is able to stay still for up to half an hour, but with young children, people with mental impairments or those in huge amounts of pain that just isn’t possible.
Revolution CT is able to produce the stunning images below in the amount of time it takes the heart to carry out one single beat, and the images it manages to collate are nothing short of miraculous. Revolution CT creates the most detailed images we’ve ever had of the inside of a living being.
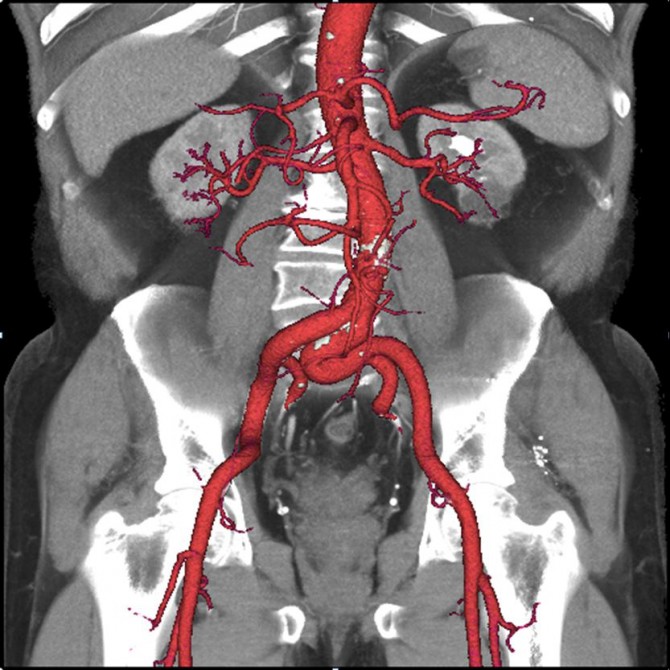
CT stands for computer tomography, it uses a series of X-ray images and stacks them into a 3D image. Revolution CT uses stabilising technology similar to that used in hand held cameras producing these crystal clear anatomical artworks.
As you scroll through the images below you have to keep reminding yourself that these aren’t just drawings or computer generated guesses, these are exactly what it looks like inside you. Utterly amazing.
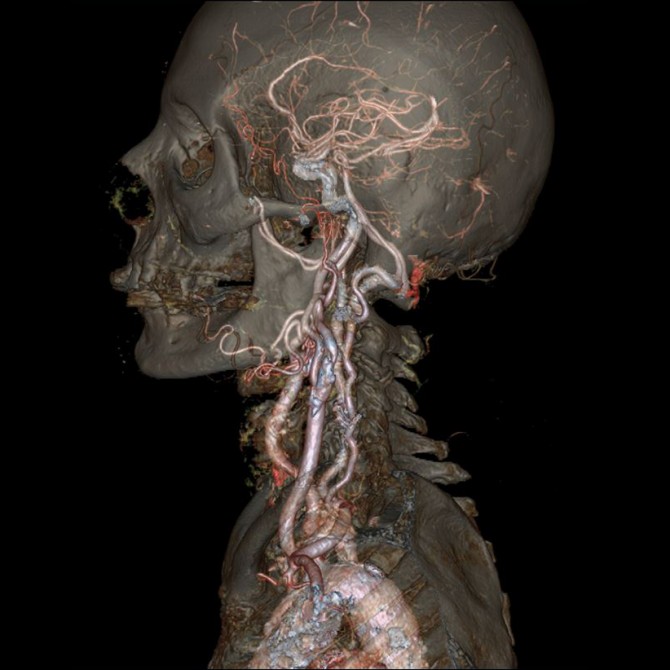
Towards the end of 2013 the Kendall Baptist Hospital in Miami were the first to use Revolution CT in the field. The hospital was more than a little impressed with its performance. Another bonus with this new technology is that it uses 82% less radiation, which is always a good thing. Here are some examples from the Kendall Baptist Hospital’s trial.
Use the arrow keys to click through the incredible images and GIFs below.
Circle of Willis
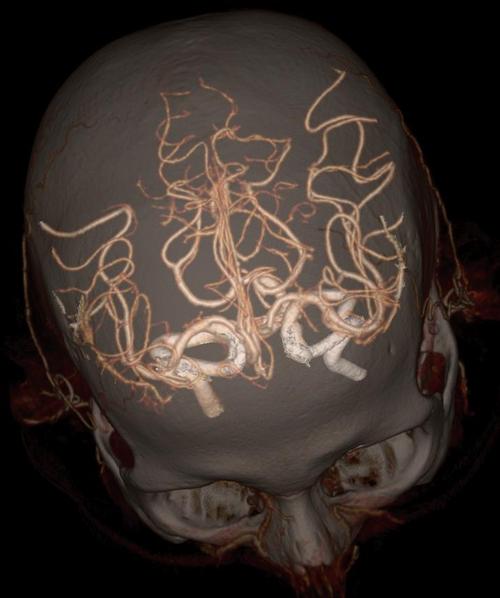
The first three images shows the circle of Willis which connects the brain’s blood supply. This little bit of tubular circuitry creates additional pathways for blood to take if a blockage should occur. It’s a kind of back up system.